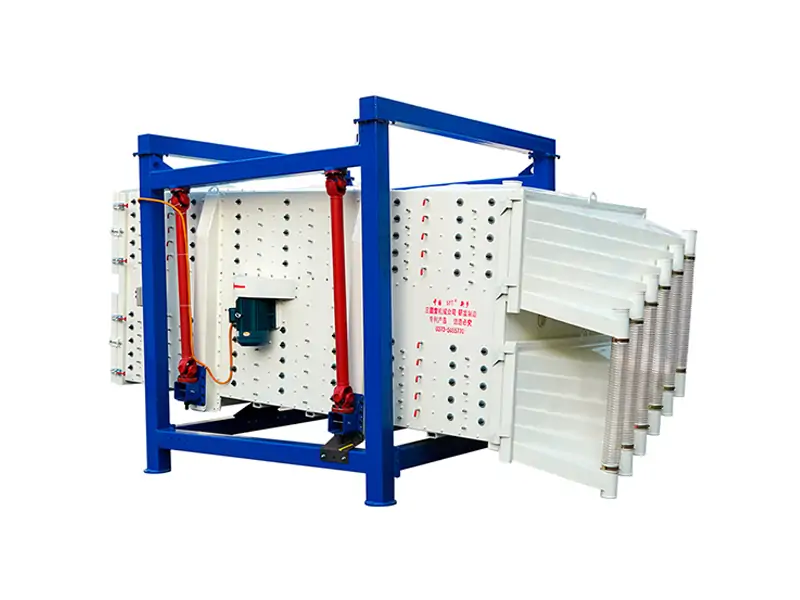
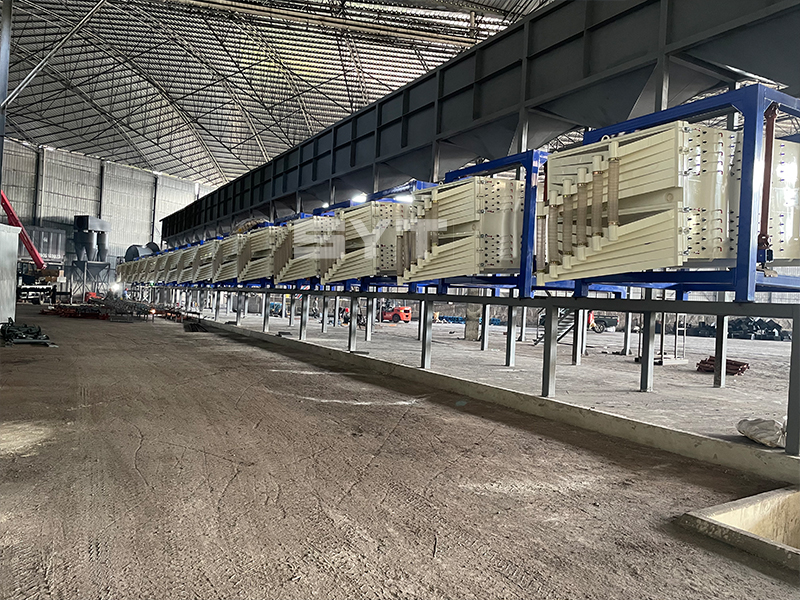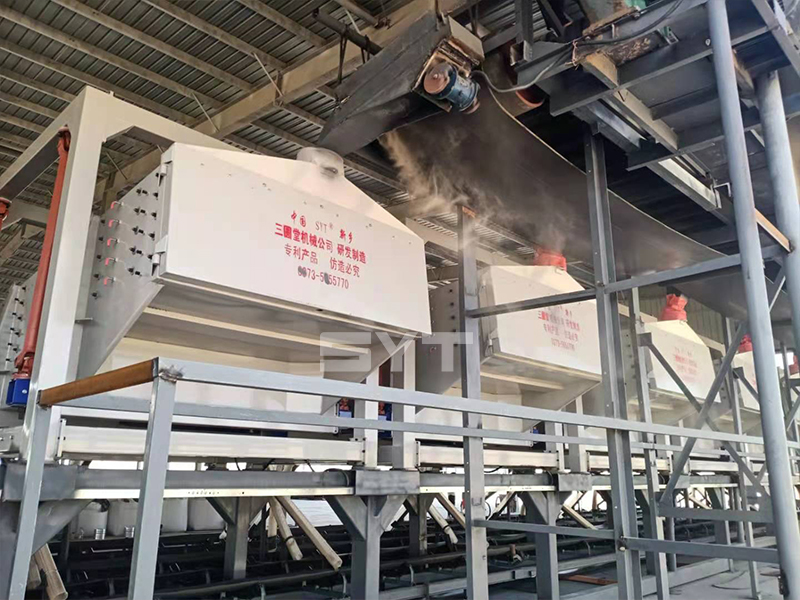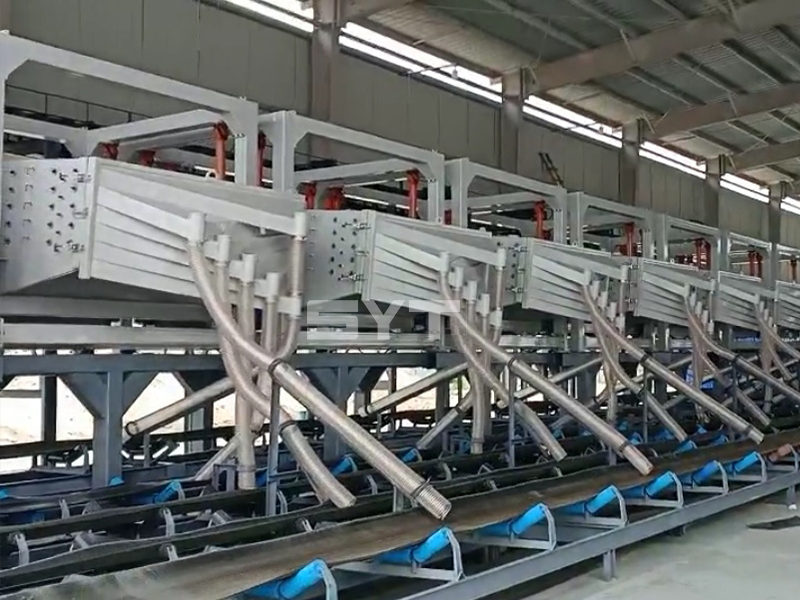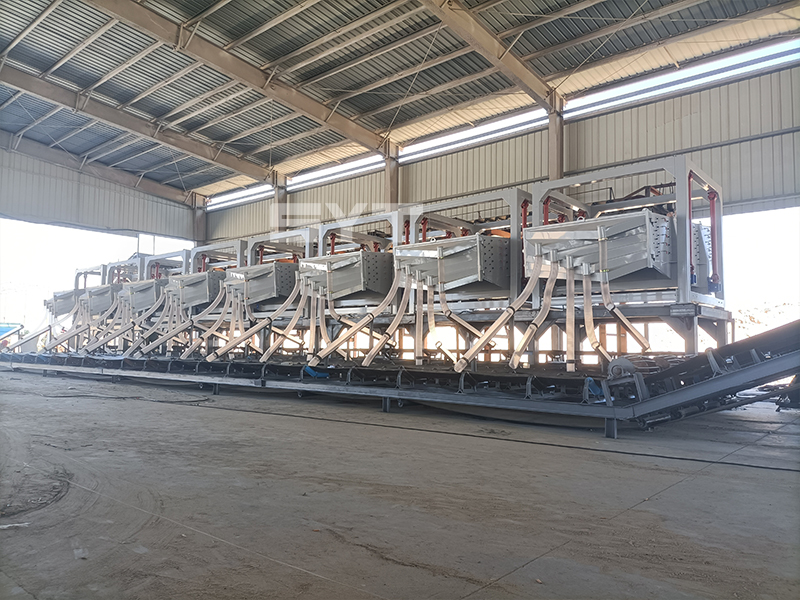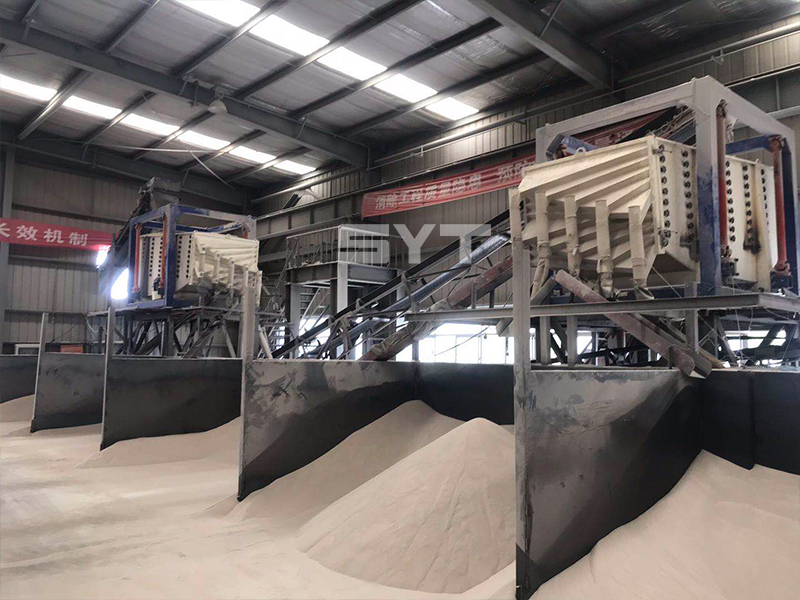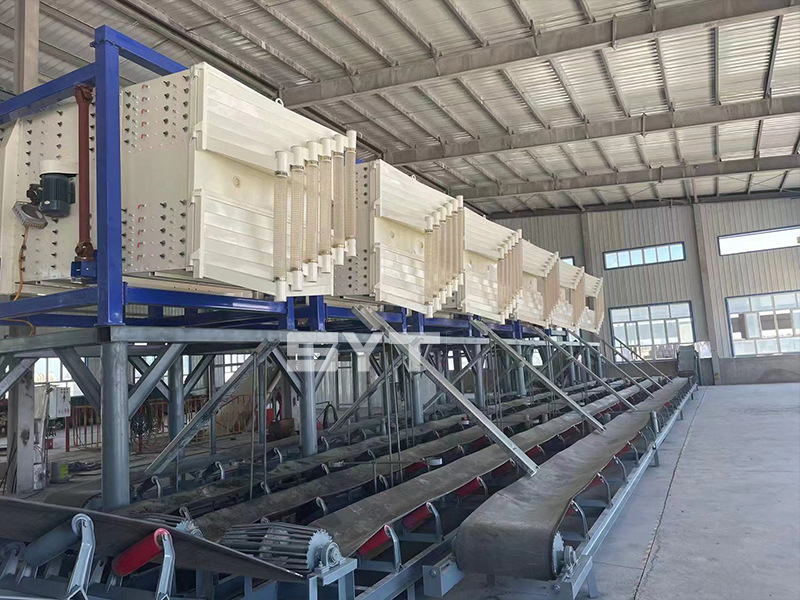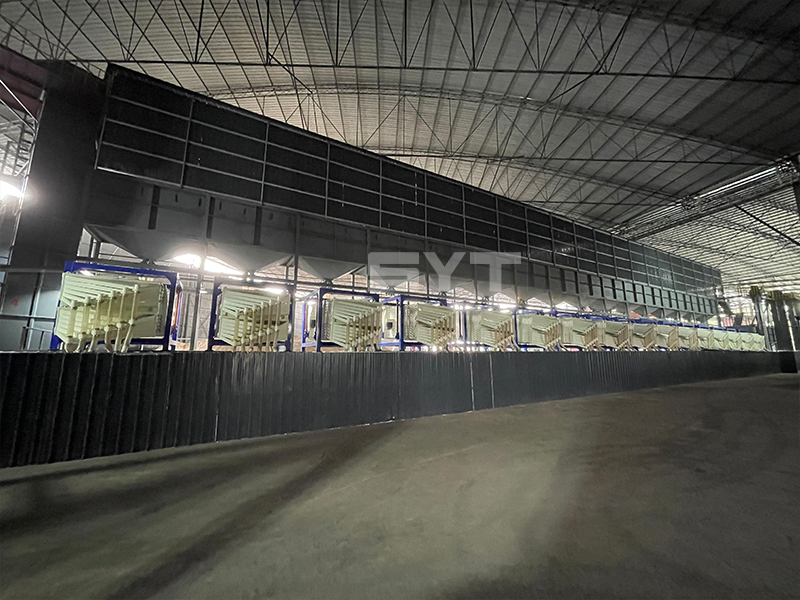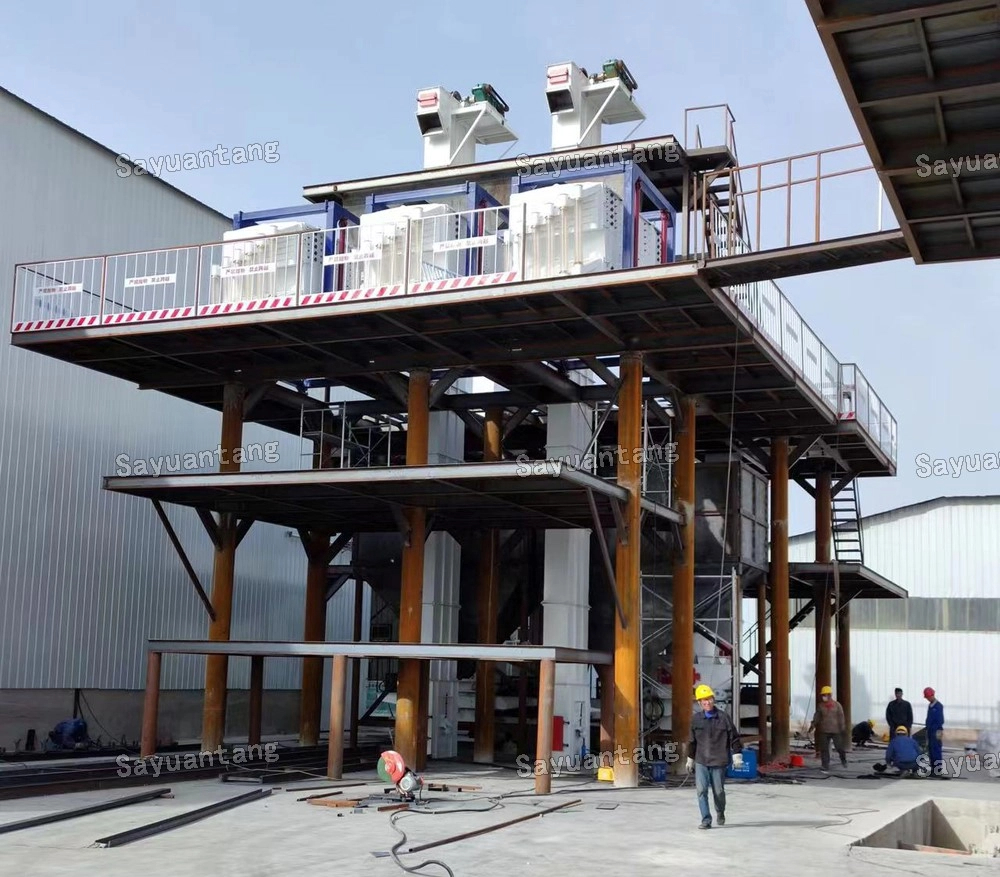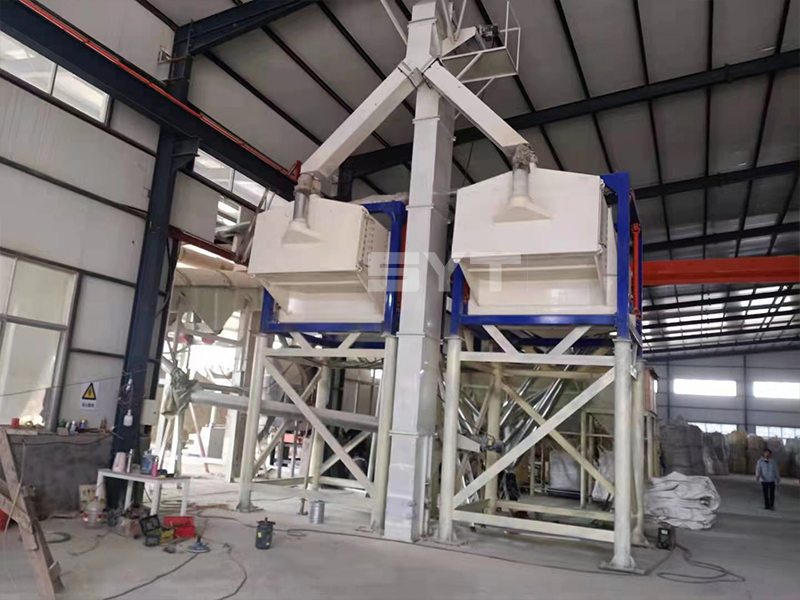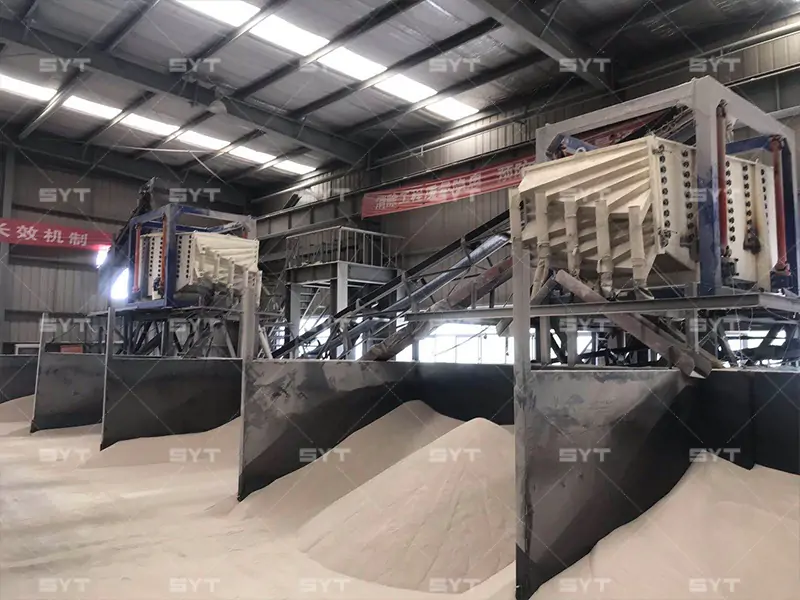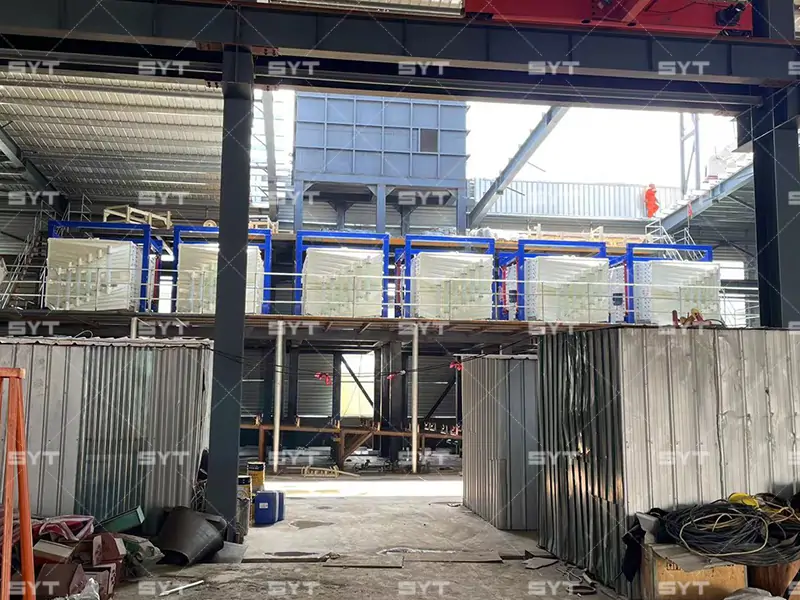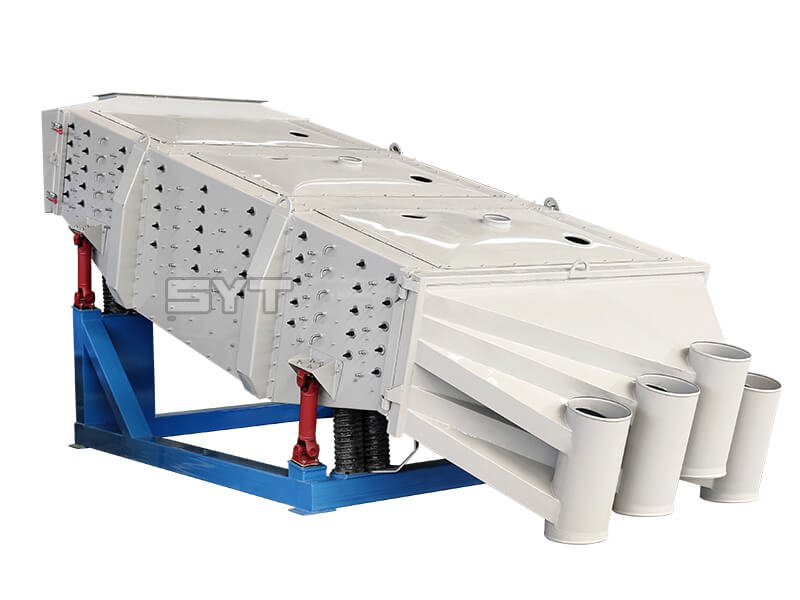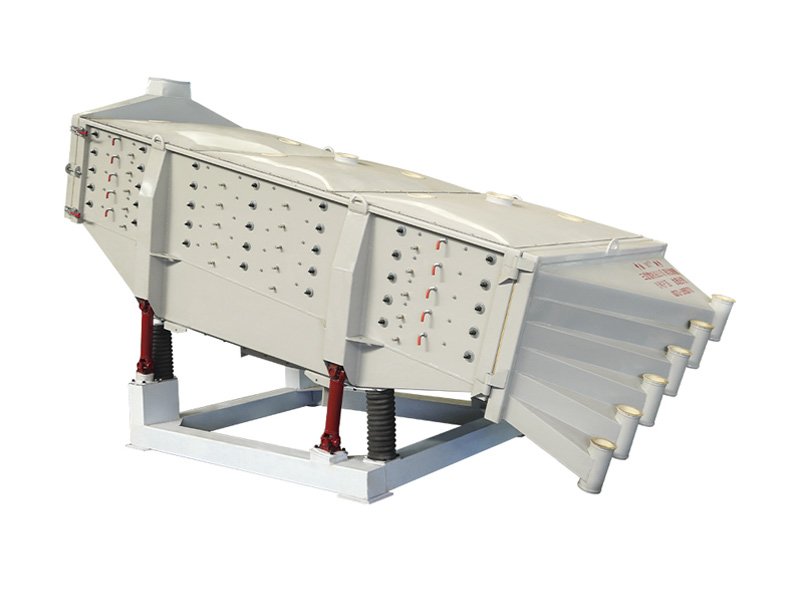
The single vibration source rectangular gyratory sifter is a standard square swing screening equipment, also called gyratory screen separator. The single-vibration design source does not have a large processing capacity as the dual-vibration source configuration, but it can provide higher screening accuracy, especially suitable for mineral powder materials with high screening accuracy requirements, such as fine screening and grading of oil fracturing sand.
- Model: FYBS-1536 , FYB-S2040
- Material: Carbon Steel
- Mesh Size: 2-300 mesh
- Layers: 1-10 layers
- Capacity: 500kg – 13 Tons/hour
Price: $14800.0 – 23400.0 / Set
Application
- Abrasive material and ceramic industry: building sand, mica, alumina, abrasive, refractory material, slurry, etc.
- Chemical industry: resin pigment, medicine, grease, paint, palette, etc.
- Food industry: sugar, salt, alkali, gourmet powder, starch, milk powder, yeast powder, pollen, food additives, etc.
- Metallurgy and mining industry: quartz sand, ore, meteorite, garnet, etc.
- Mechanical industry: casting sand, powder metallurgy, electromagnetic material, and metal powder, etc.
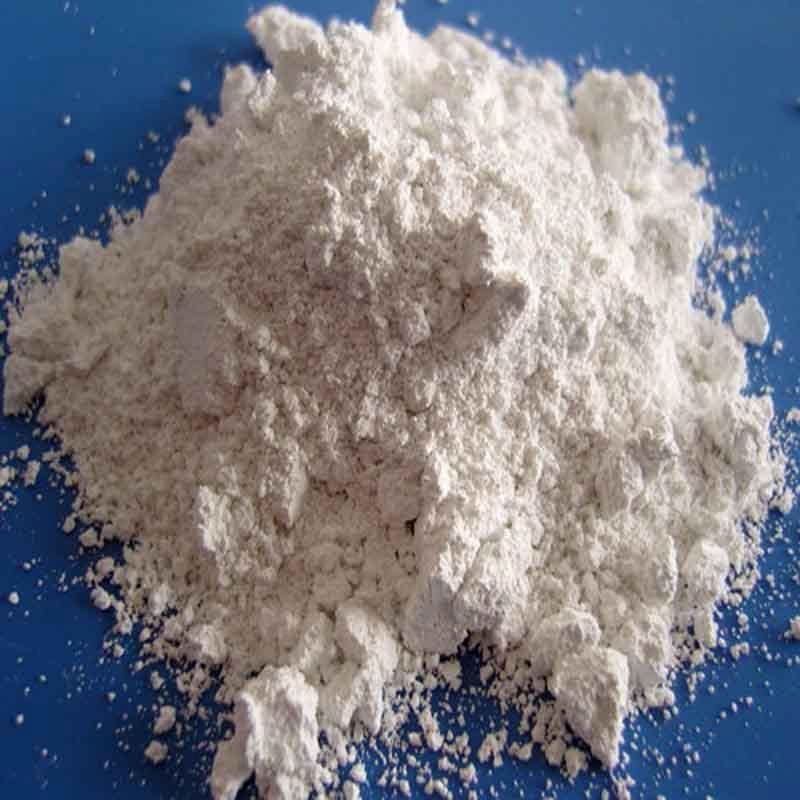
 Silica Sand
Silica Sand Ceramic sand
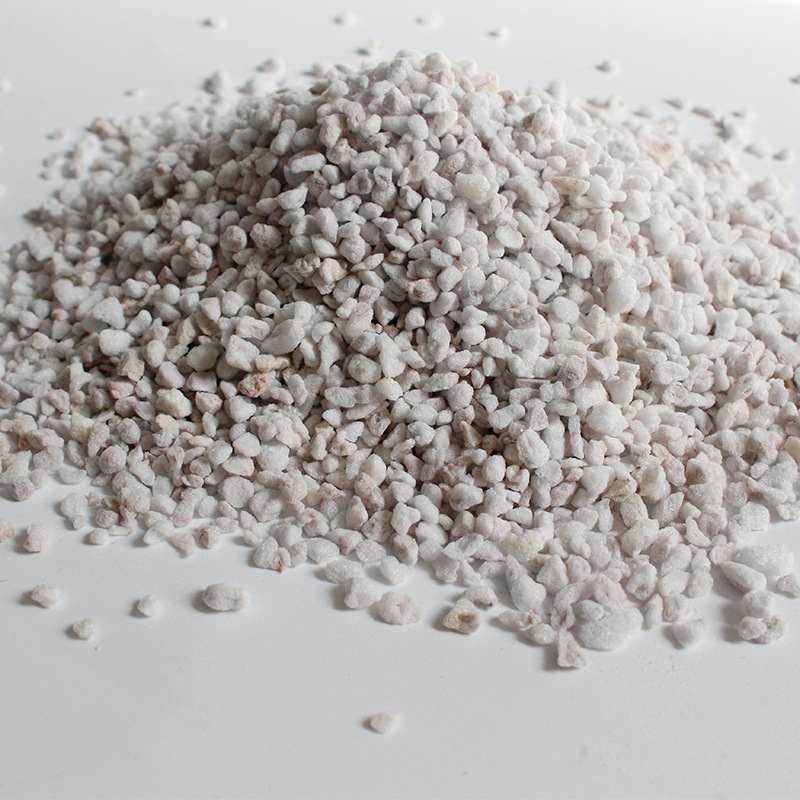
Ceramic sand Perlite
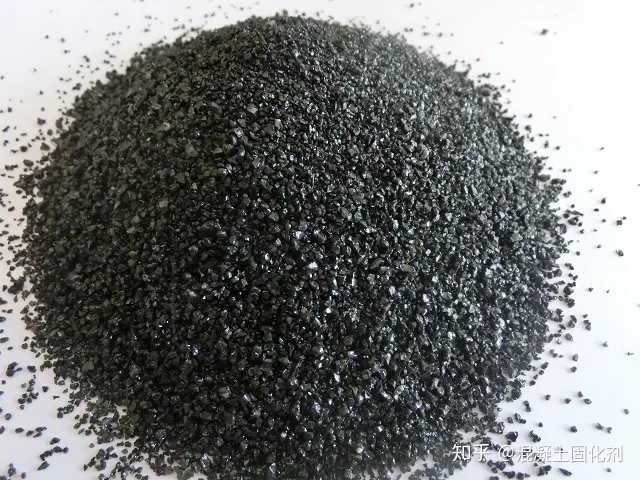
Perlite Emery
Emery Metal Silicon Powder
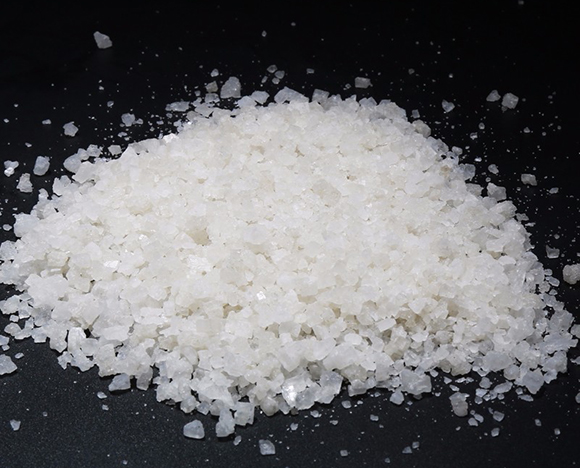
Metal Silicon Powder Industry Salt
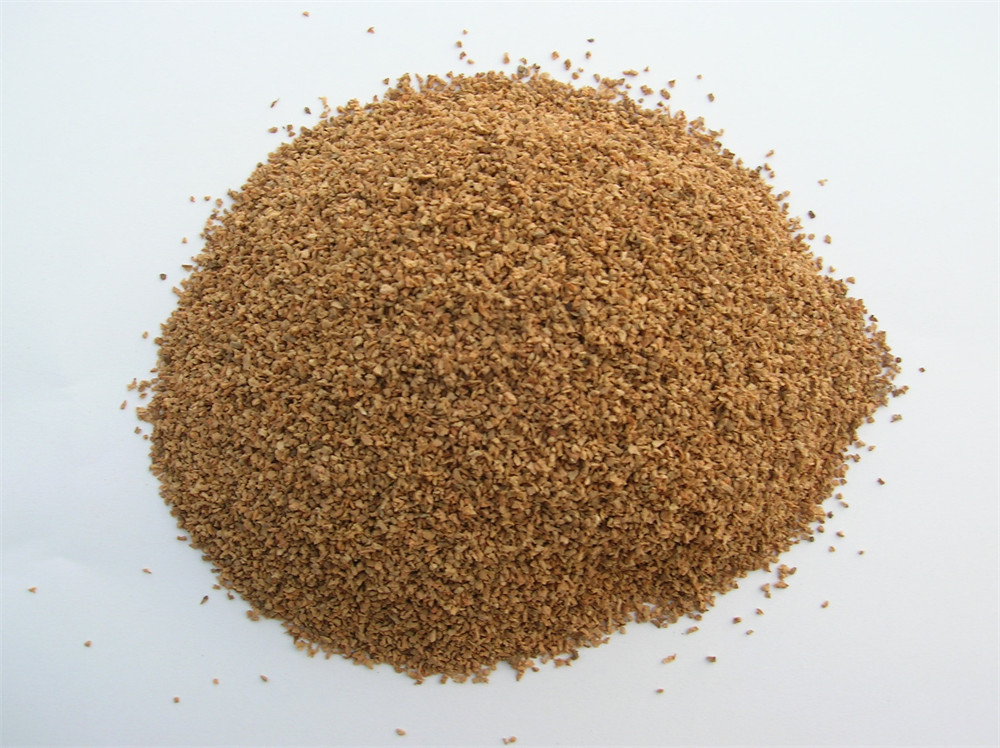
Industry Salt Cork powder
Cork powder Calcium Carbonate
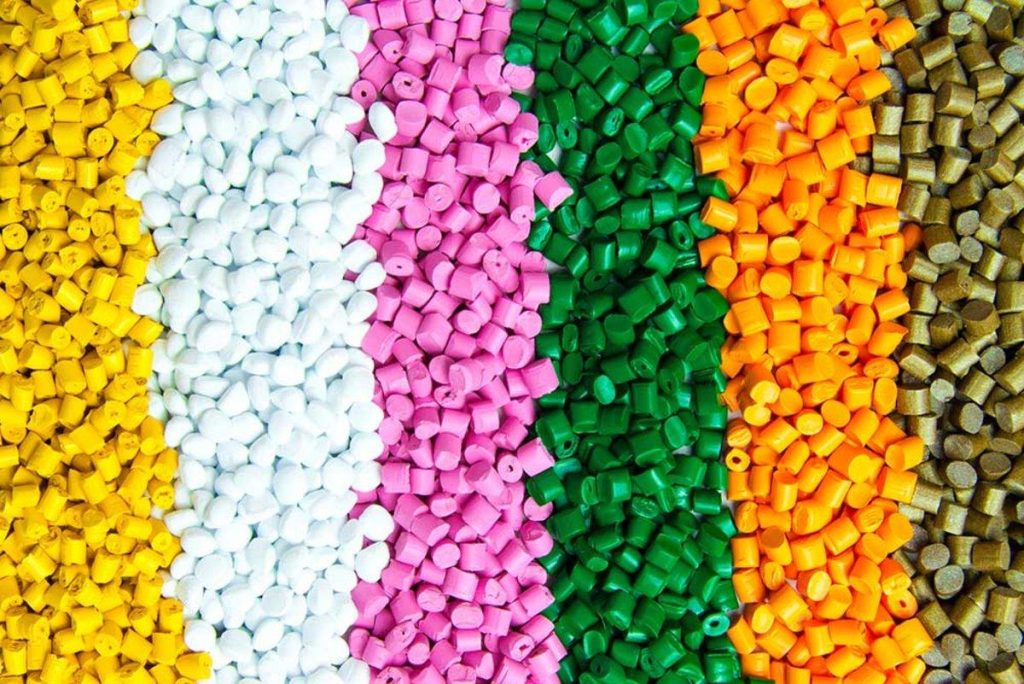
Calcium Carbonate Plastic particles
Plastic particles
Working Principle
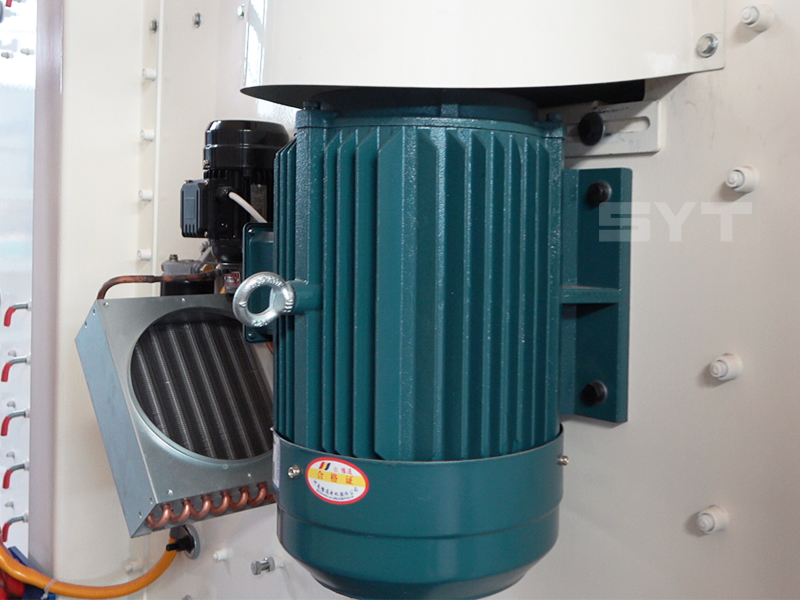
The essence of the single vibration source rectangular sifter is the reciprocating inertial force formed by the rotation of the eccentric wheel winding the dead axle. According to the structure characteristics and working principle of a rotex gyratory screener, the screen surface is arranged with a level or incline (the angle of inclination is 0-5 degrees). After turning on the gyratory sifter, the screen box takes reciprocating movement under the inertial force, screen box drives the screen surface to make periodic shaking, which makes the materials on the screen surface make a directional jumping movement with the screen box.
During the period, the material less than the screen aperture falls to the layer, and the material bigger than the screen aperture makes a jumping movement, discharged from the coarse outlet.
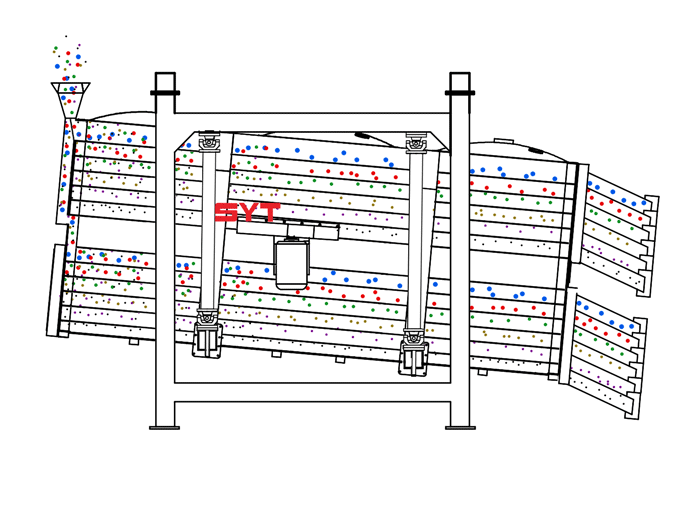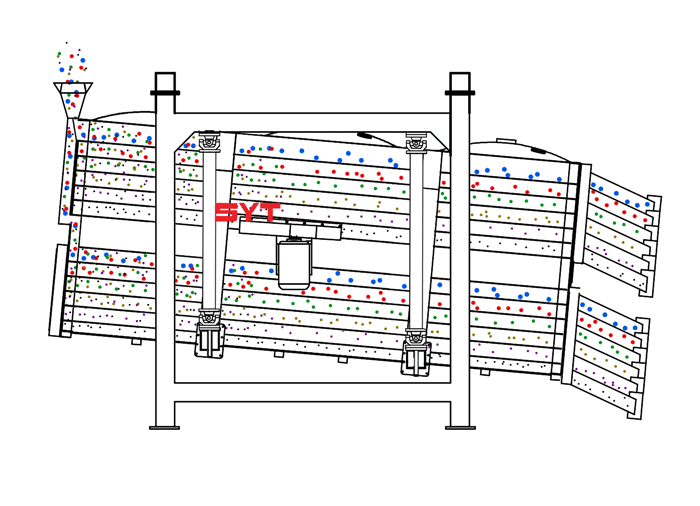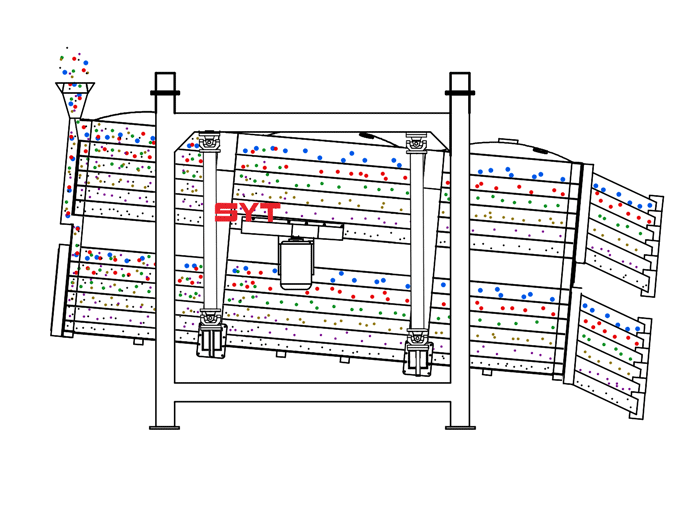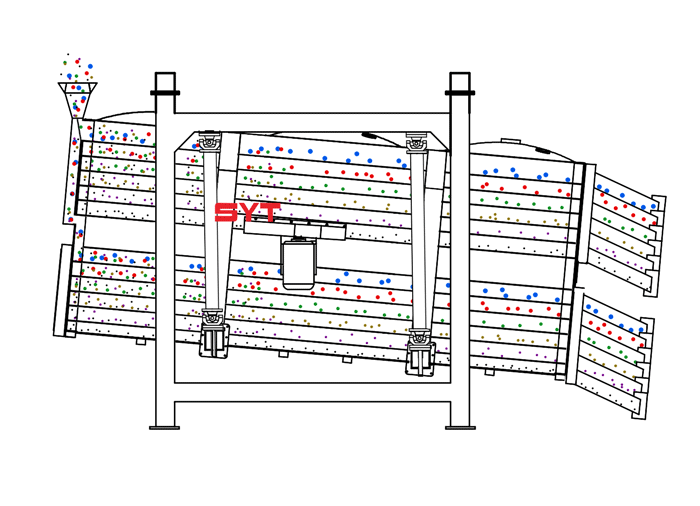
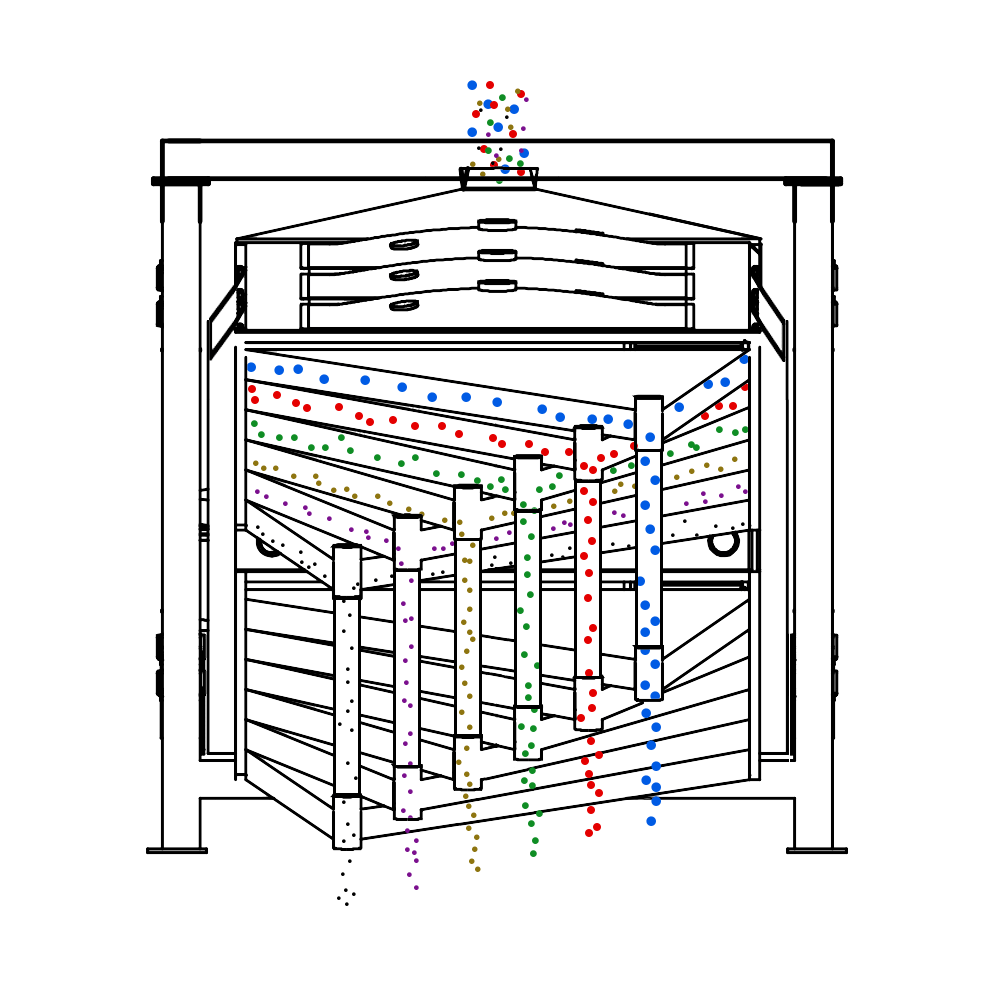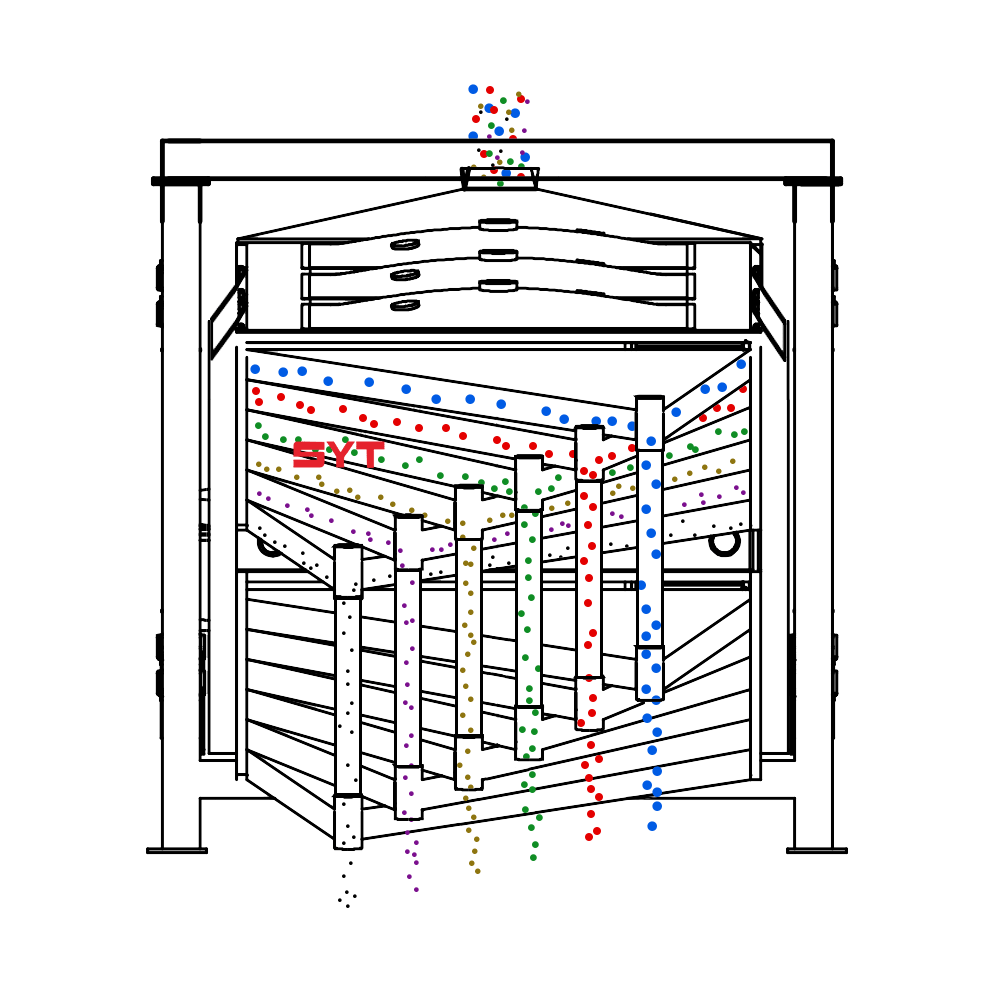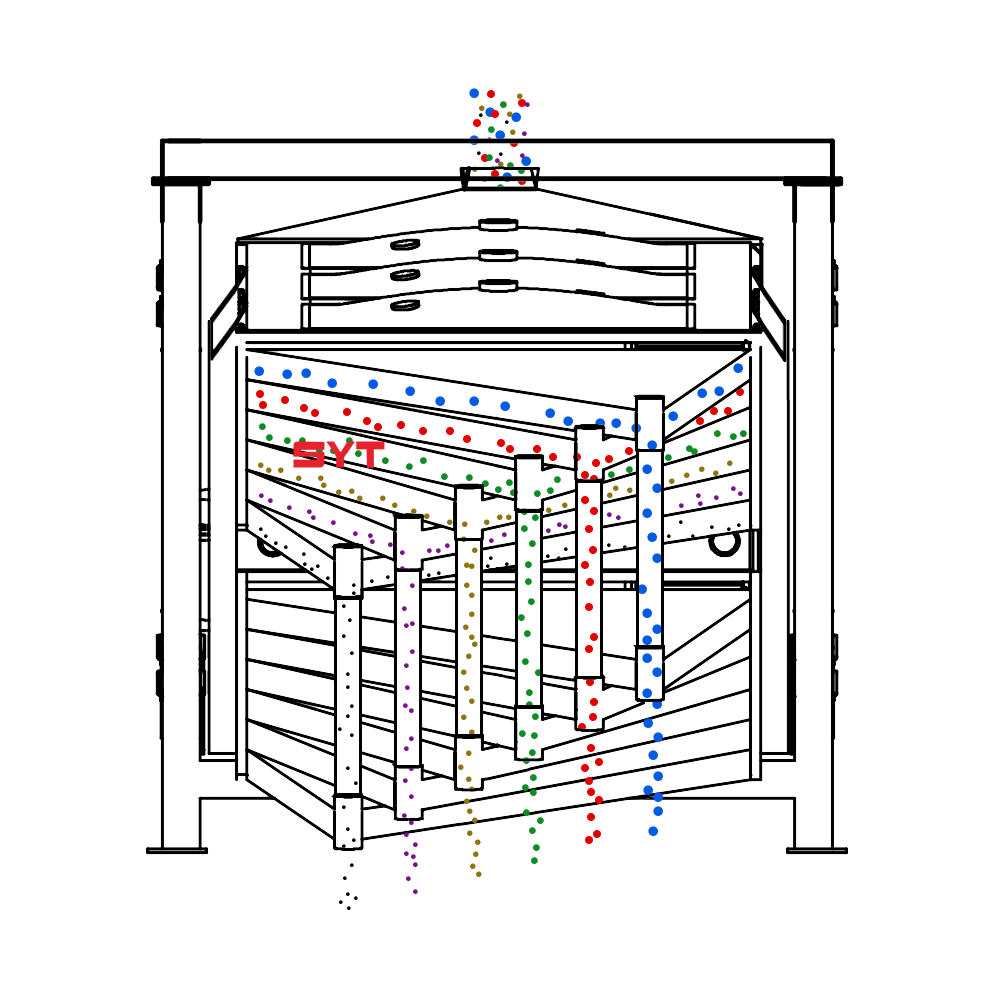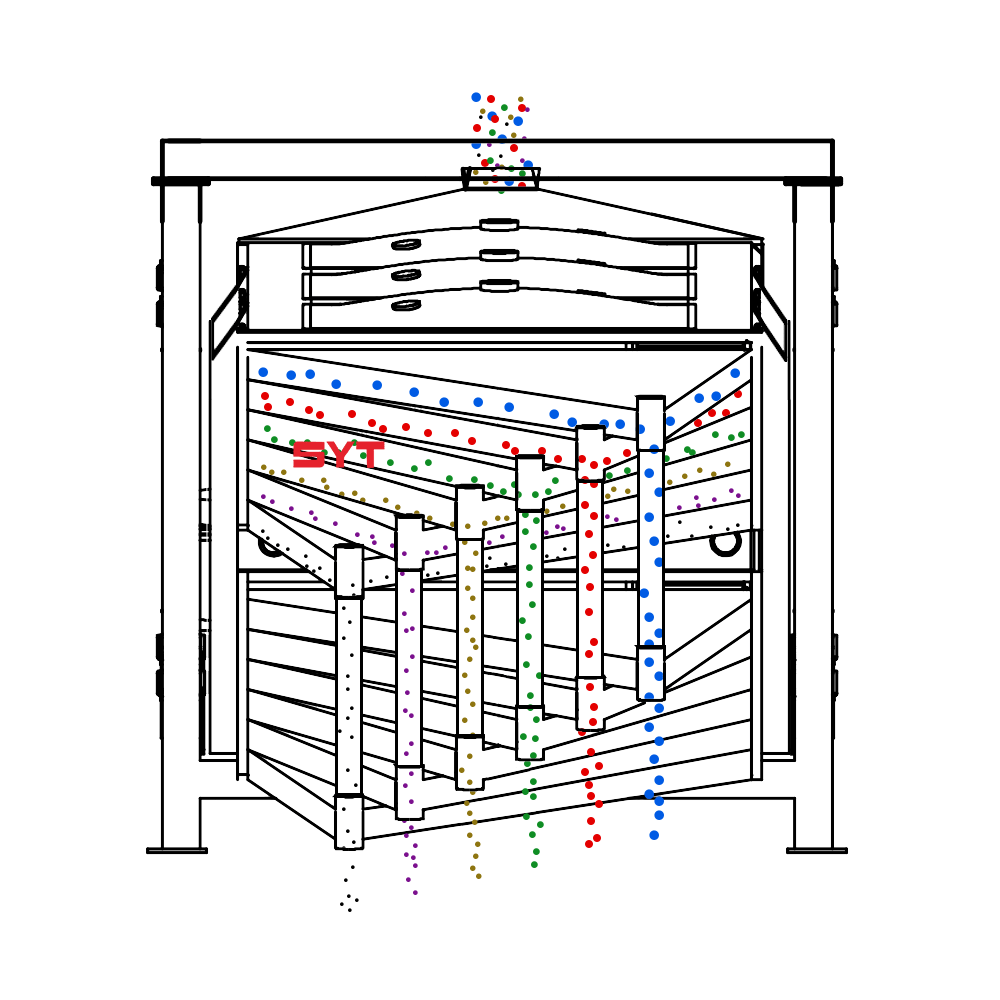
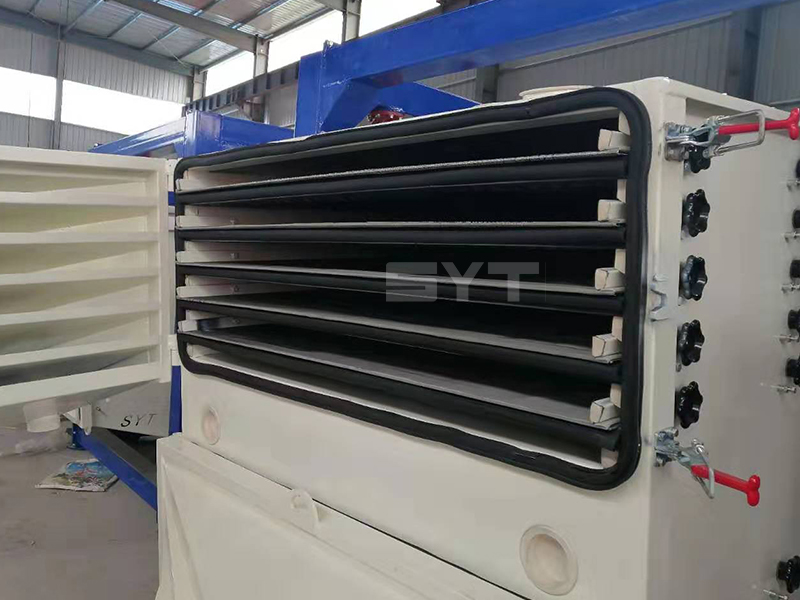
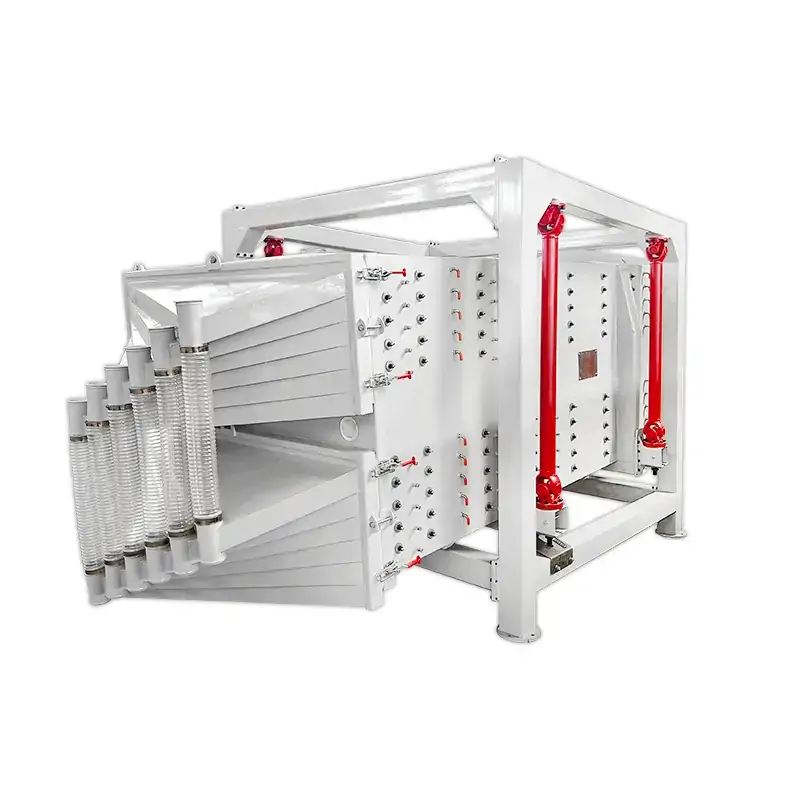
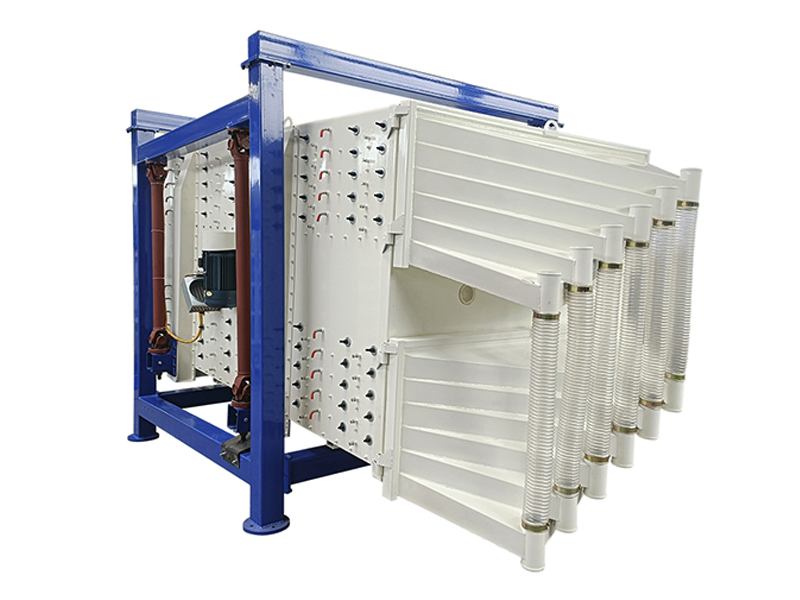
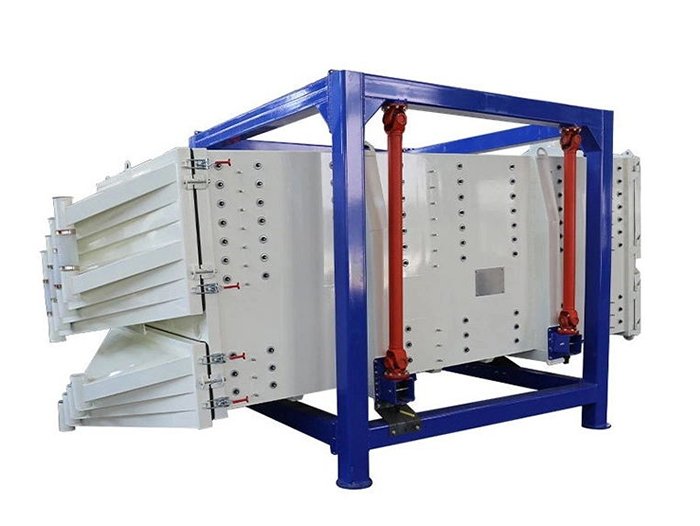
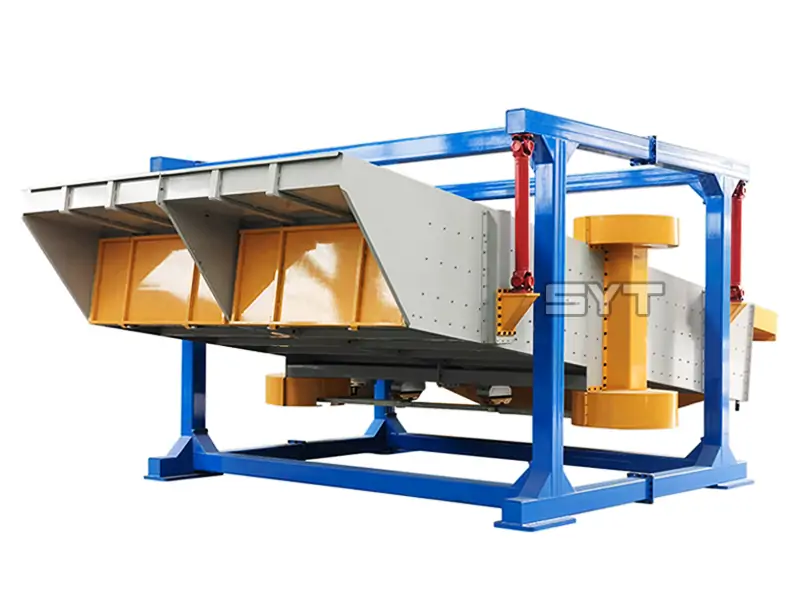
Structures
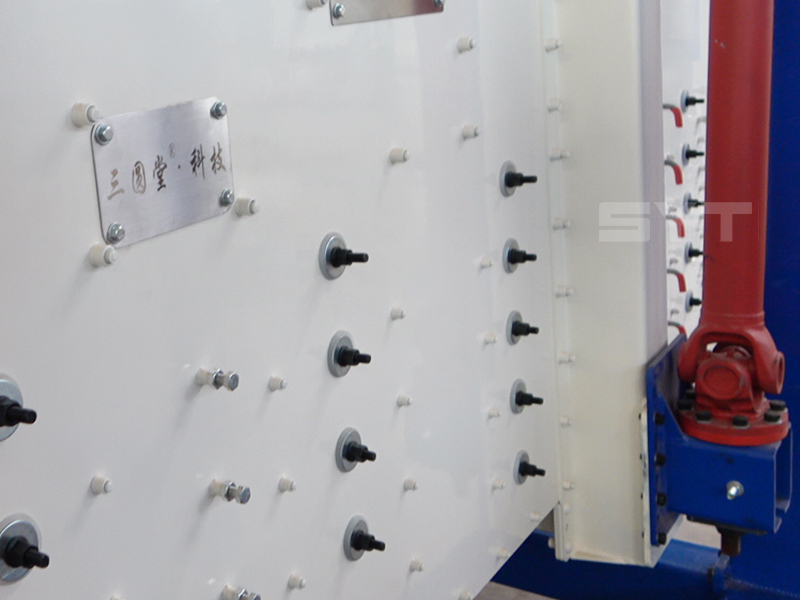
This equipment is a rectangular gyratory sifter FYBS model developed and produced by our company with a hanging structure. It has applied for several national protection patents and is leading the industry.
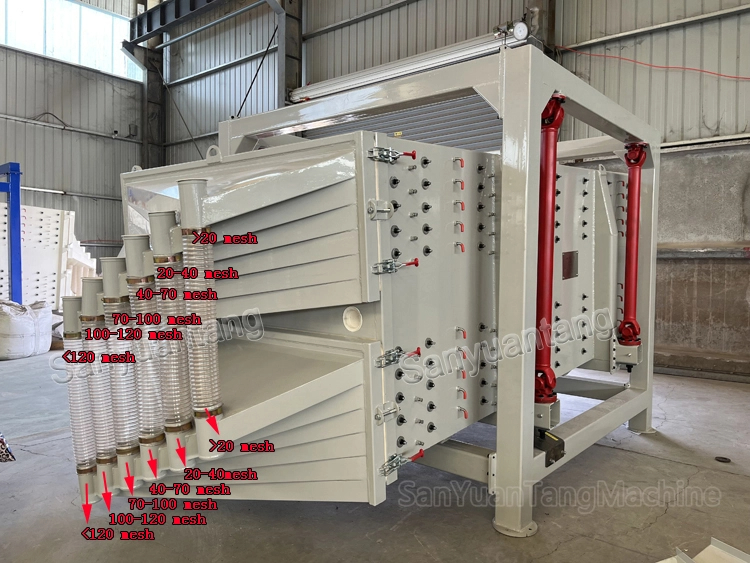
The screen frame and the screen mesh installation method adopt a unique and innovative design, making the installation very convenient. Usually 9-layer design can be divided into 10 grades at one time, or 4 layers + 4 layers equivalent to 2 sets sieve machine, or 2 layers + 2 layers + 2 layers equivalent to 3 sets sieve machine, Or designed as 1 layer +1 layer +1 layer +1 layer +1 layer is equivalent to 5 sets sieve machines.
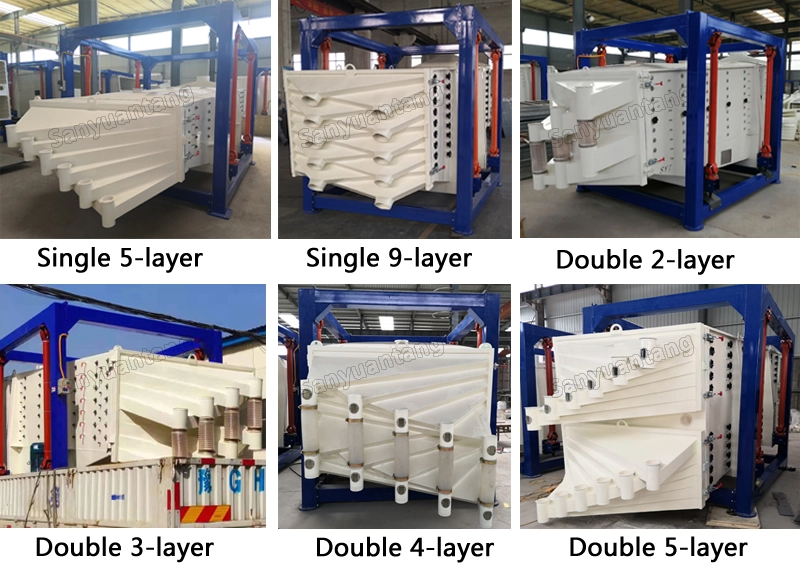
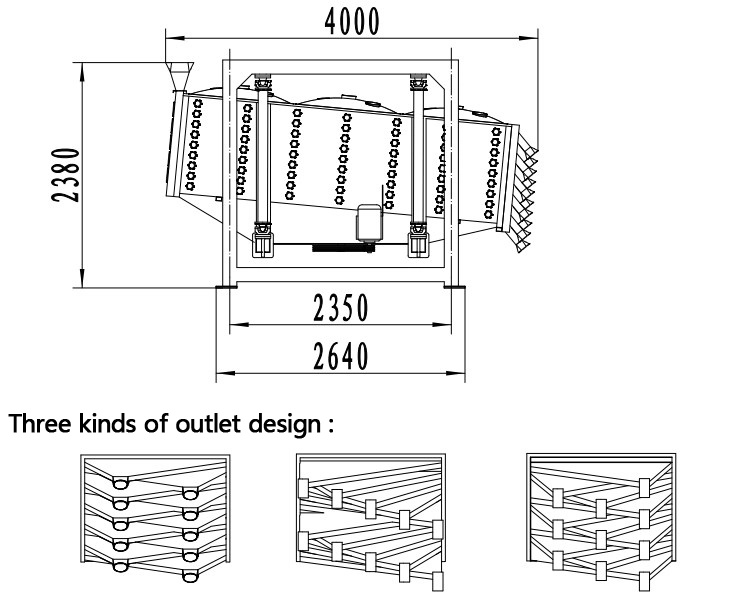

Details
Specifications
| Model | Screen size | Screening area | Screen inclination | Layers | Power | Number of turns | Case travel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FYBS1536 | 1.5*3.5 m | 4.5-9 m2 | 5-8 | 1-10 | 5.5 | 180-260 | 25-60 mm |
| FYBS2040 | 2.0*4.0 m | 8-9 m2 | 5-8 | 1-10 | 7.5 | 180-260 | 25-60 mm |
Features
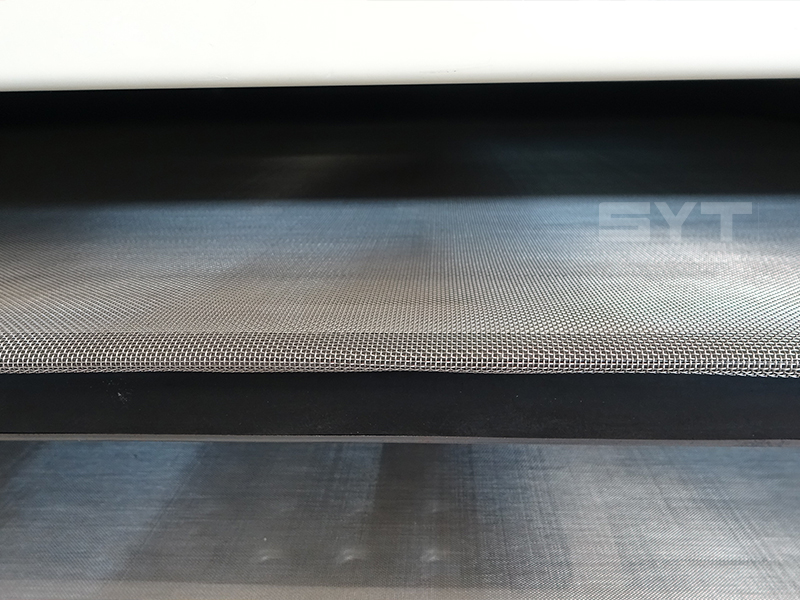
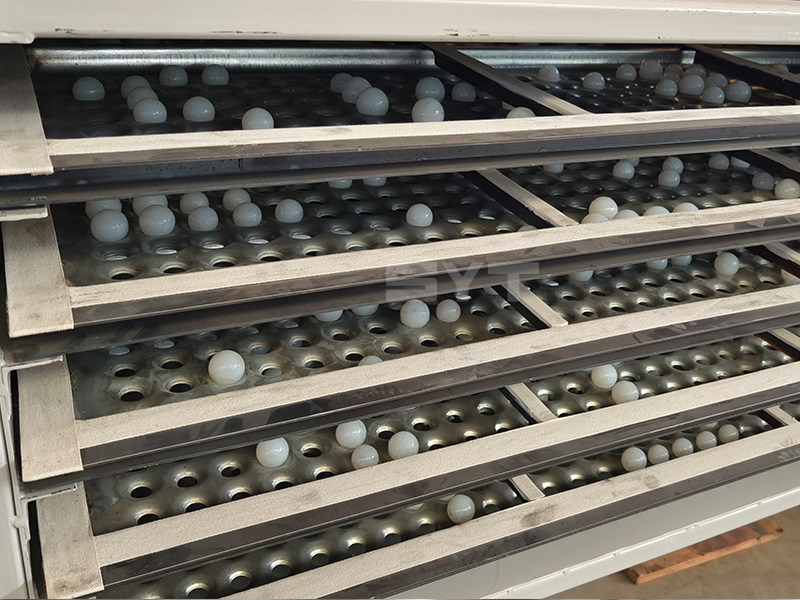
- The screen mesh frame and the screen mesh and bouncing balls installation method adopt a quick open design and are easy to install,5-10 minutes to replace the screen mesh, which can be performed from the feed of the machine. Reducing equipment downtime and increasing production capacity.
- Diameter 40 mm bouncing balls to clean sieve mesh.
- Discharge port: The height can be customized. The color is optional.













































