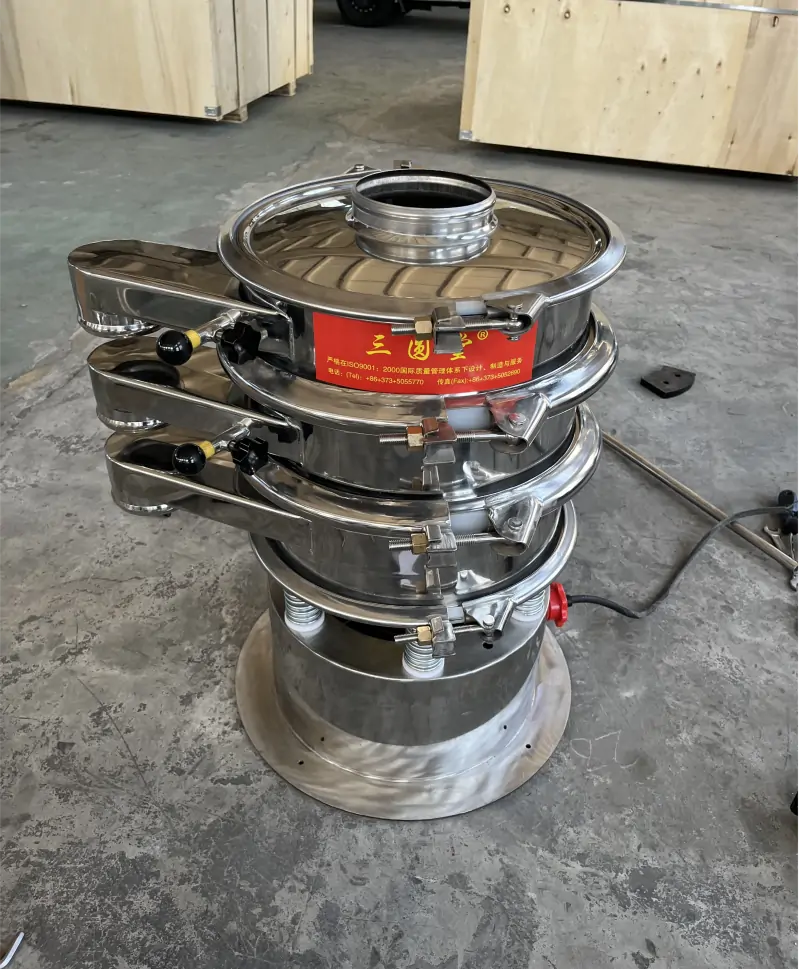
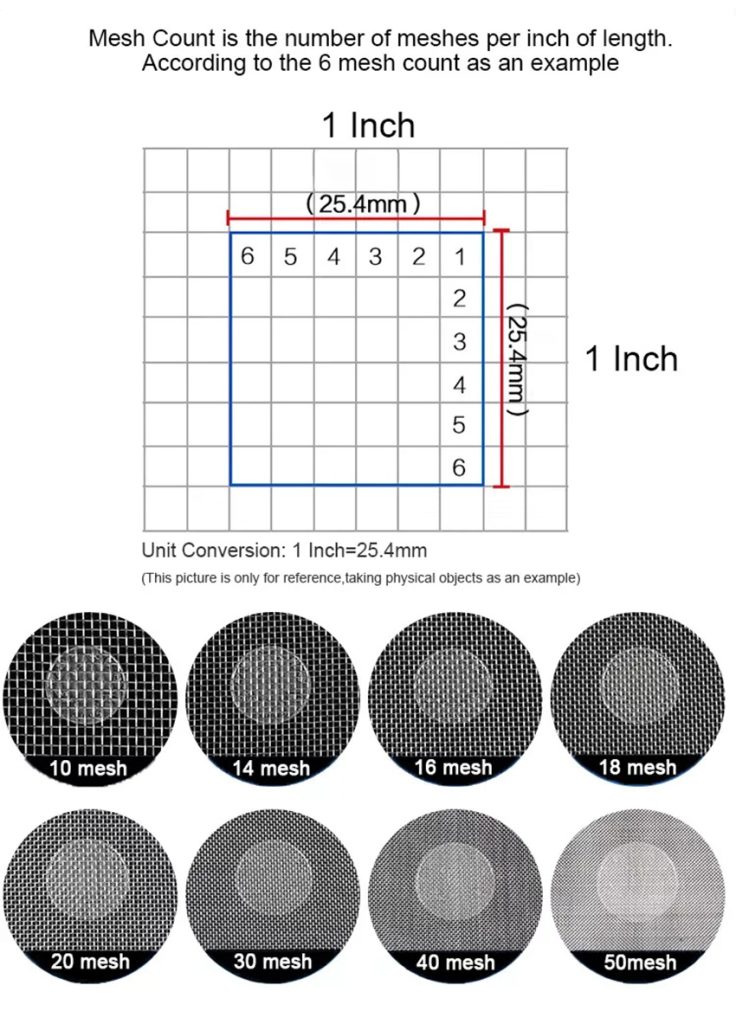
Sieves are essential tools in laboratory settings, available in various shapes and sizes to separate materials into distinct grades based on particle size. Typically made from woven wire mesh, often steel, test sieves are integral to industries like cement, construction, chemicals, food, pharmaceuticals, light industry, and mining. Standard test sieves are commonly used in laboratories for precise particle analysis. But how many different types of sieves are available on the market? In the following sections, we will explore the classification and applications of the different types of sieves.

What Are Sieves?
A sieve is a tool or device used to separate, screen, or filter particles of different sizes. It usually has a porous screen surface, which is covered with holes of uniform or different sizes, and the size of these holes determines the size of the particles that the sieve can filter out. The sieve is usually made of metal (such as stainless steel, copper, iron, etc.), plastic, or ceramic, and is commonly round, square, or rectangular. The choice of specific material depends on the purpose of the sieve, the working environment, and the required service life.
Different Types of Sieves
There are several different types of sieves, each suited to a specific purpose depending on the industry and application.

Woven Wire Sieves
Wire woven sieves are usually made of stainless steel wire. They have high strength and durability, can withstand greater screening pressure and wear, are corrosion-resistant and high-temperature-resistant, have a smooth surface, are easy to clean and maintain, and are suitable for long-term, high-intensity screening operations.
Perforated Plate Sieves
Perforated plate sieves have a solid plate with precise holes punched through it. Unlike wire sieves, which have flexibility in their mesh, perforated plate sieves are rigid and are commonly used in industries that require higher durability and precision, such as the food industry for sieving grains or powders.
Electroformed Sieves
Electroformed sieves are created by depositing metal onto a form to create extremely fine mesh structures. These sieves are highly precise and are often used in applications where particle size needs to be controlled to an extremely tight tolerance, such as in chemical or pharmaceutical production.
What Are the Different Standard Sieves?
Standard sieve is the equipment used for screening granular materials. It is usually composed of a screen frame and a screen mesh. The size, design, and manufacture of standard sieves follow certain national or international standards to ensure the reliability and repeatability of the screening results. Therefore, the manufacturing and classification of standard sieves are as follows:
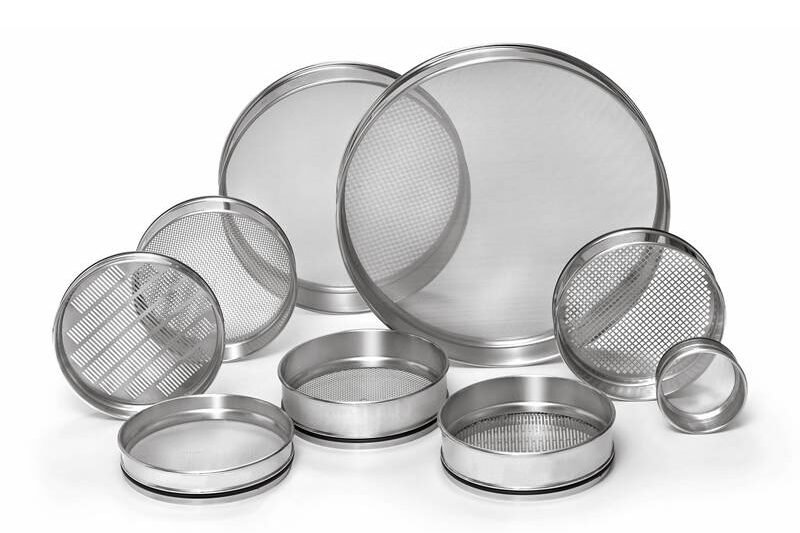

ISO 3310
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) specifies standards for test sieves. ISO 3310-1 deals with metal wire mesh test sieves, while ISO 3310-2 covers perforated plate test sieves. These standards ensure that the sieves are manufactured to precise specifications regarding aperture size and mesh quality.
ASTM E11
In the United States, the ASTM E11 standard is commonly followed. This standard outlines the specifications for wire cloth and sieves used in test methods for determining particle size. It defines different mesh sizes and tolerances to ensure uniformity and precision in testing procedures.
BS 410-1:2000
This is a British Standard that specifies the sizes of openings for test sieves. The standard covers both wire mesh and perforated plate sieves, providing consistency in the classification of particle sizes for industrial applications.
4 Types of Sieves
While there are many different types of sieves, four key types are frequently used in industrial and laboratory settings:
Test Sieves
Test sieves are used for precise particle size analysis and are often found in laboratory environments. These sieves are manufactured to strict standards, such as ISO and ASTM, and come in a variety of sizes to suit different testing needs. Test sieves are commonly used in pharmaceutical industry and laboratory.
Grain Sieves
Grain sieves are used in agriculture and food production to separate and grade grains based on size. These sieves often have perforated plates or woven mesh designed to handle larger particles, such as wheat, corn, or rice.
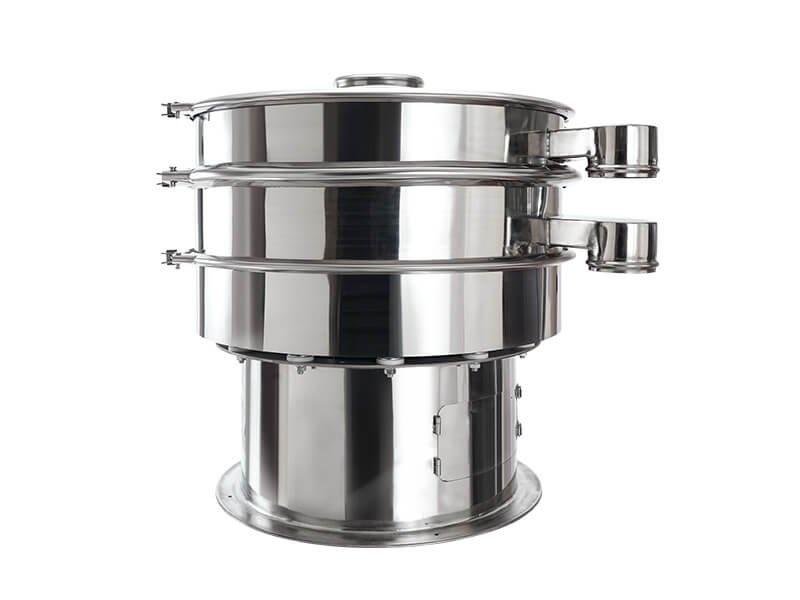
Industrial Sieves
These sieves are designed for heavy-duty use in industries such as construction, mining, and mineral processing. Industrial sieves are often larger and more robust than laboratory sieves, and they may be used in conjunction with vibrating screen equipment to sift large quantities of material efficiently.
Pharmaceutical Sieves
In pharmaceutical production, the precision of the drug is important. Therefore, sieves are mainly used to filter powders required for tablet manufacturing or to screen raw materials to ensure uniformity. Usually, electroformed and woven wire screens with fine mesh are used.
| Type of Sieve | Typical Use | Material | Mesh Size Range | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Woven Wire | Lab & Pharma | Stainless steel | 0.02–2 mm | Fine powders & precise screening |
| Perforated Plate | Food & Grain | Steel/Aluminum | 0.5–10 mm | Grains, powders, heavy materials |
| Electroformed | Pharma & Chemicals | Nickel | 0.02–0.2 mm | Extreme precision particle control |
| Coarse Industrial | Construction & Mining | Steel | 2–50 mm | Sand, gravel, aggregates |
Custom sizes and materials are available – contact us for a quote.
3 types of sieve Shakers
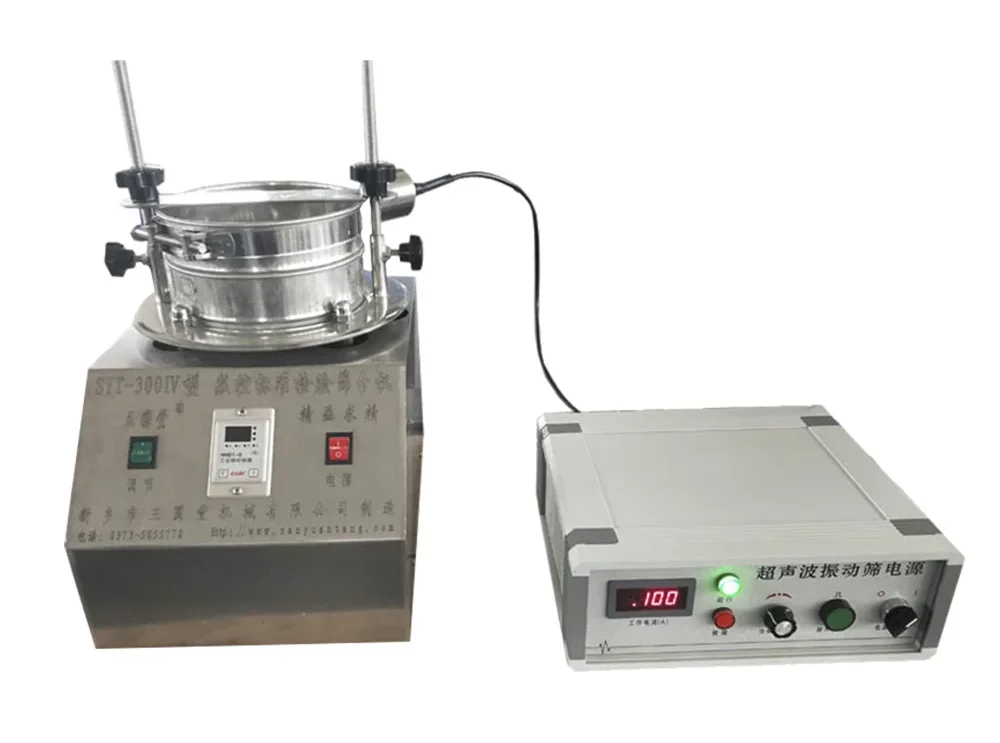
Ultrasonic test sieve shaker
Features: It is a special sieving machine suitable for food, chemical, pharmaceutical and other industries, with high efficiency and accurate screening effect.
Slap-type standard sieve Shaker
Such as BSJ-200, it screens by slapping and vibrating, and is suitable for pharmaceutical powders and particles of different particle sizes.
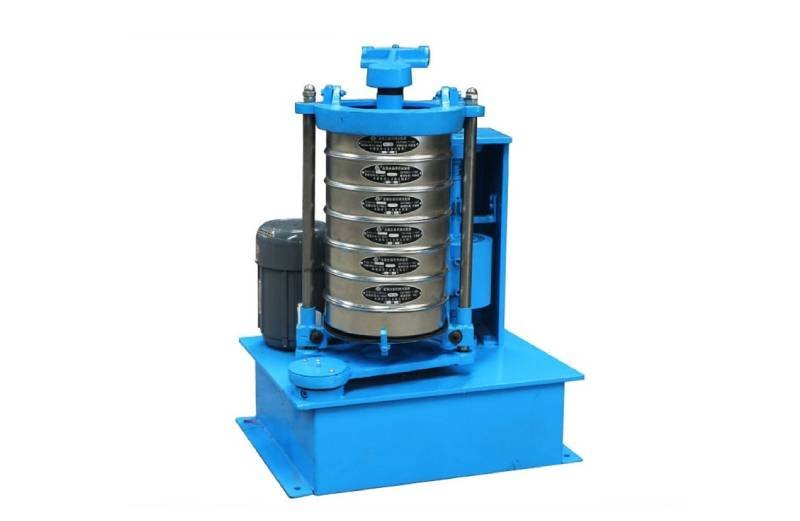

Vibrating sifter
It improves screening efficiency through vibration mechanism, is suitable for screening fine particle materials, and is widely used in laboratories and production in the pharmaceutical industry.
Types of Sieve Sizes
Sieves come in various sizes, measured by the size of the mesh openings, also known as aperture sizes. The size of the aperture determines which particles pass through and which are retained. Here’s a breakdown of common sieve sizes:
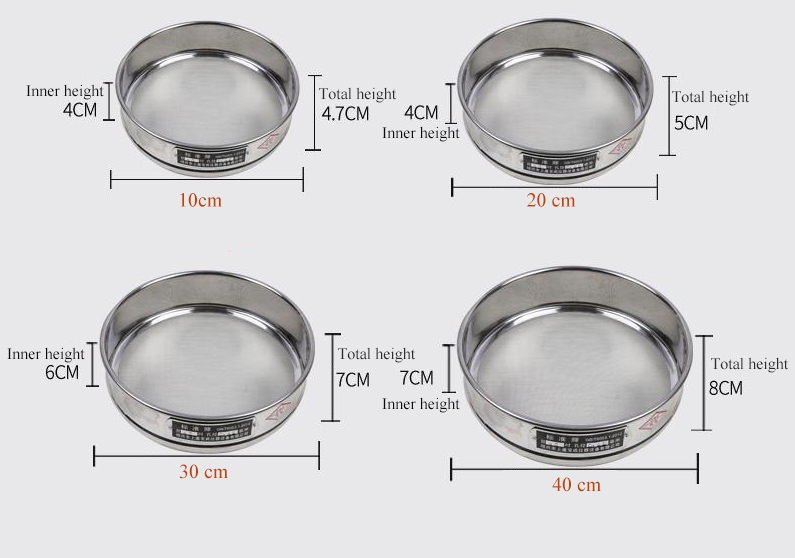

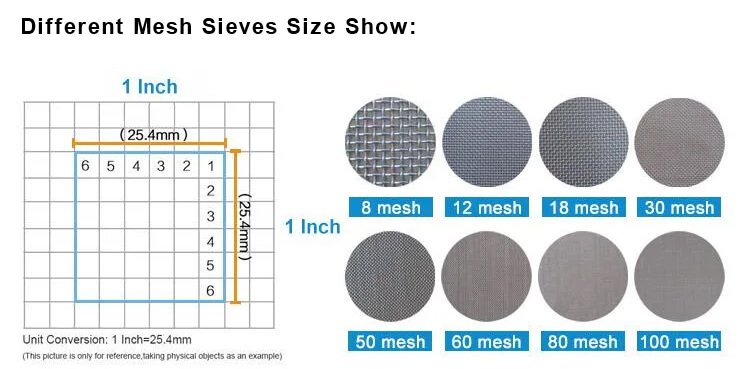
Fine Mesh Sieves (0.02 mm to 0.2 mm)
These are used for very fine powders and particles, often in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries. Fine mesh sieves are ideal for sieving delicate materials that require a high level of precision.
Medium Mesh Sieves (0.2 mm to 2 mm)
Medium mesh sieves are versatile and are commonly used in food production, agriculture, and general industrial applications. They can handle a wider range of particle sizes and materials.
Coarse Mesh Sieves (2 mm to 50 mm)
Coarse sieves are robust and designed to handle heavy materials, such as gravel, sand, and aggregates, in the construction and mining industries. They are used for sorting larger materials like these.
Sieve Uses
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Sieves are commonly used in the pharmaceutical industry for particle size analysis, impurity detection, and solid content testing.
- Food Industry: In the food industry, sieves are commonly used to grade and remove impurities from raw materials such as flour, powdered sugar, and grains.
- Construction Industry: In the construction industry, sieves are commonly used to screen and grade sand and gravel, as well as other construction materials to remove impurities and debris.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of sieves, their sizes, and the analysis methods used can help industries ensure consistent product quality. Whether for pharmaceuticals, food, or construction materials, choosing the right sieve is critical to achieving the desired results. By adhering to standard sieve sizes and employing the appropriate type of sieve analysis, industries can maintain control over their production processes and deliver high-quality products.

Reach out to our team to find the perfect sieve solution for your industry
Email: info@sanyuantang.com
Phone: +86-18639095165